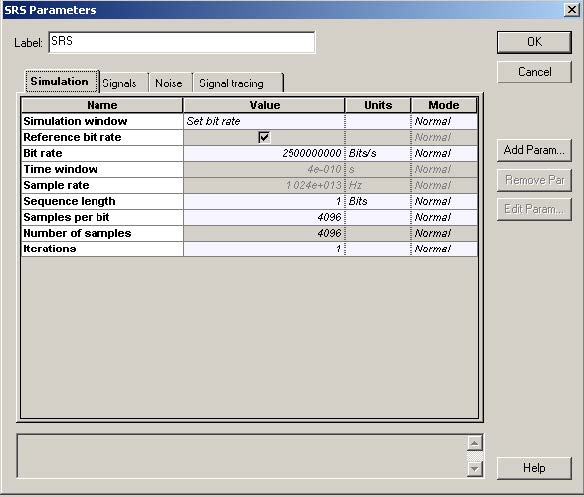
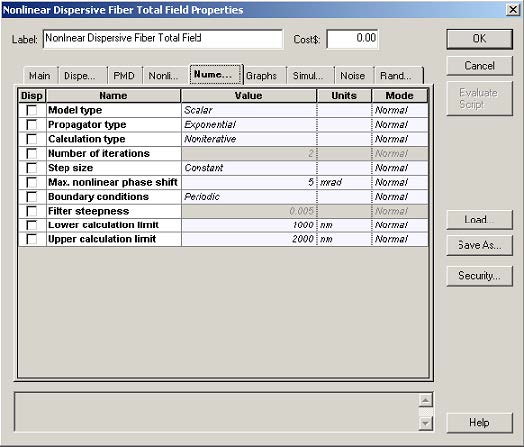
This lesson demonstrates the light amplification caused by the stimulated Raman scattering effect. The layout and its global parameters are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Layout and global parameters
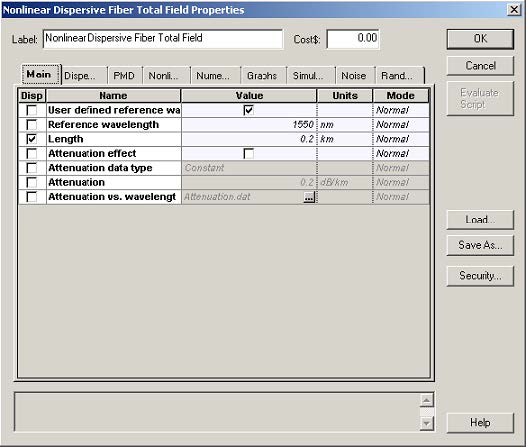
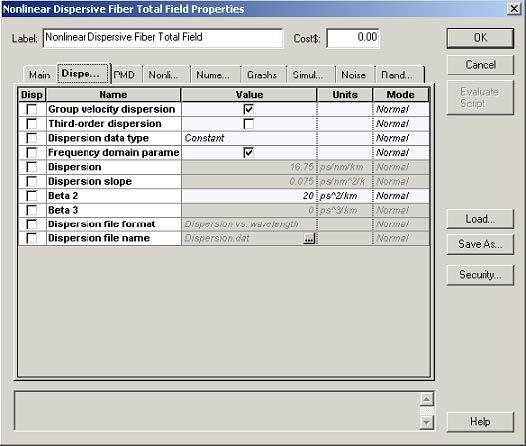
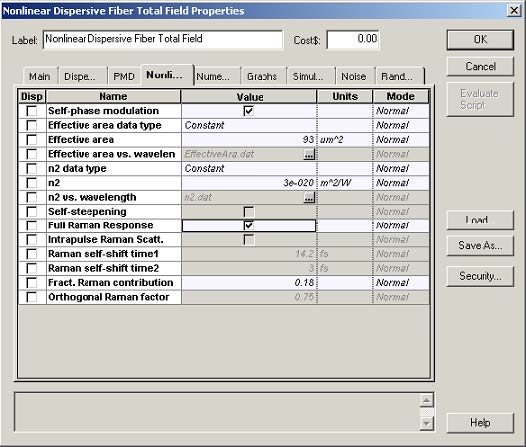
Figure 2 shows the setup for the optical fiber component.
Figure 2: Setup parameters
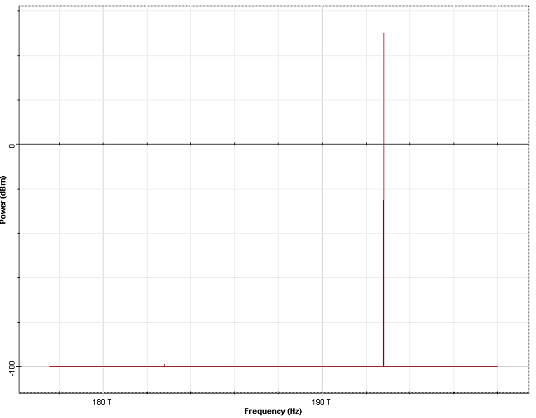
The spectrum of the input signal consists of a strong pump monochromatic wave (100 W) at 1550 nm and a weak (-99 dBm) Stokes wave at 1640 nm (10 THz Stokes shift) (see Figure 3).
Figure 3: Input signal spectrum
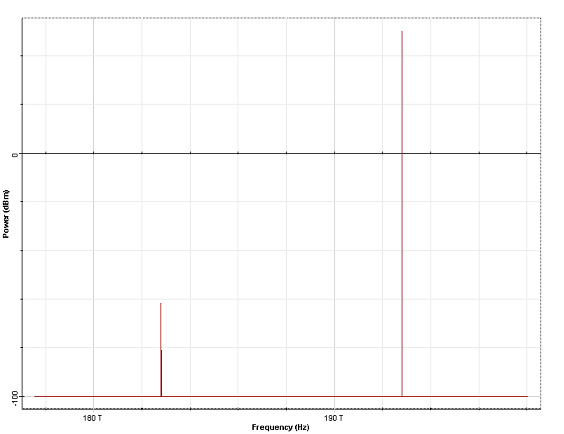
Figure 4 gives the output spectrum. The weaker (low frequency) spectral component is amplified and the gain is G=99-61.7=37.3 dB.
Figure 4: Output signal spectrum
Raman gain coefficient is given [1] by:
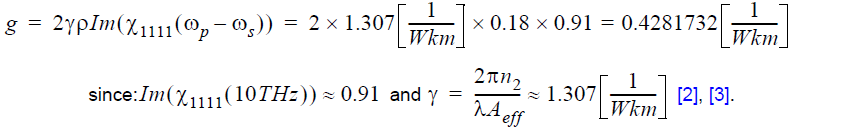
The Raman gain (in dB) is then G = 10log(exp(gPL)) = 37.2dB, where P is
the pump power and L is the fiber length.
References
[1]G. P. Agrawal, “Nonlinear fiber optics”, Academic press, 3rd edition, 2001.
[2]R. W. Hellwarth, Prog. Quant. Electr. 5, 1 (1977).
[3]P. Tchofo Dinda, G. Millot, and S. Wabnitz, JOSA B, 15, 1433, (1998).