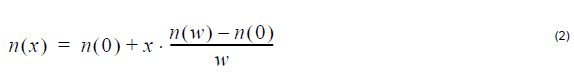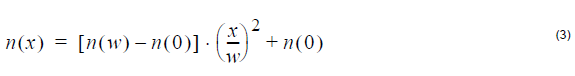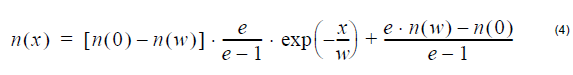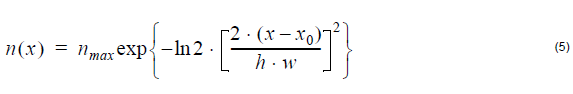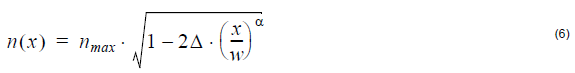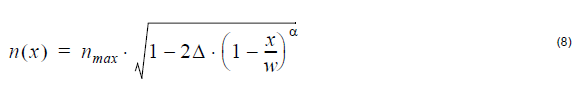The radial distribution of the fiber refractive index is called the index profile. In the
case of a slab waveguide, the transverse refractive index is called the index profile.
The index profile determines guiding properties of the fiber or slab waveguide. In
general, the core region has a higher index than the cladding region. However, the
index profile can have regions where the index is lower than the cladding value.
Modern fiber or slab waveguide designs are based on index profiles that assure
proper operation within a range of wavelengths.
For example, a dispersion flattened fiber design involves a few concentric index
regions.
In OptiGrating 4.2, regions define a fiber or slab waveguide profile. Each region has
its dimension (width) and refractive index profile. The default refractive index profile
options are listed below, where x is the region’s local coordinate, w is the width of the
region.
Constant index profile:
Linear index profile:
Parabolic index profile:
Exponential index profile:
where n (0), n (w) is the refractive index at x=0 and x=w, respectively.
Gaussian index profile:
where nmax is the maximum index value x0 is the peak position, and h is the
normalized value of FWHM
Alpha-peak index profile:
where nmax is the maximum index value, and Δ is the normalized index difference.
The difference is defined as
Alpha-dip index profile:
where nmax is the maximum index value, and Δ is the normalized index difference.